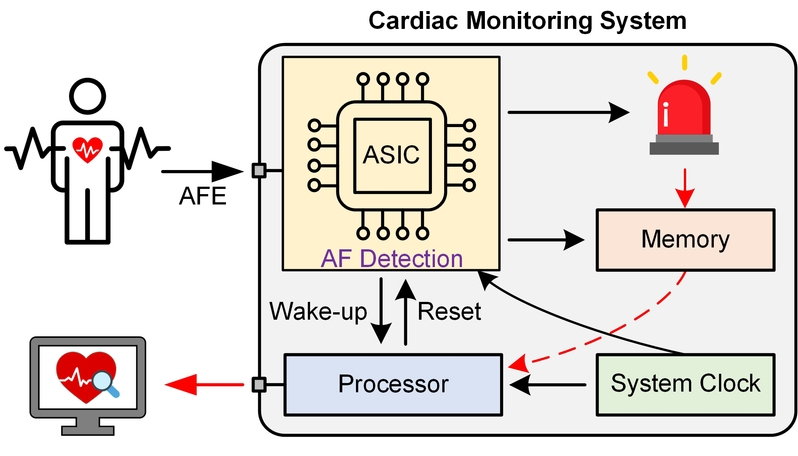
本文介绍了一种用于房颤(AF)检测的事件驱动心脏监测系统,通过低功耗ASIC和后端处理器的协同设计。只有在检测到AF异常时,ASIC才会从待机模式唤醒处理器,后者通过UART接口将AF事件从前端SRAM传输到PC。随后,处理器重新进入待机模式以减少功耗。提出了一种改进的Pan和Tompkins算法,与传统设计相比实现了49.7%的功耗降低。基于R峰检测和KS检验的AF诊断算法被实现为一个ASIC,在0.18μm CMOS技术中实现,并实现了92.45%的AF检测灵敏度。该系统显示了实现下一代可植入式心脏监测系统的潜力。
This paper presents an event-driven cardiac monitoring system for atrial fibrillation (AF) detection through the codesign of a low-power ASIC and a back-end processor. Only when the AF abnormality is detected, the ASIC wakes up the processor from the standby mode, which transfers the AF episode from a front-end SRAM to the PC through a UART interface. Afterward, the processor reenters the standby mode to reduce power consumption. An improved Pan and Tompkins algorithm is proposed which achieves 49.7% power reduction compared with the conventional design. The R-peak detection and KS-test-based AF-diagnosis algorithms are implemented as an ASIC in a 0.18-μm CMOS technology and achieve an AF-detection sensitivity of 92.45%. The system shows promise for realizing the next-generation implantable cardiac monitoring systems.