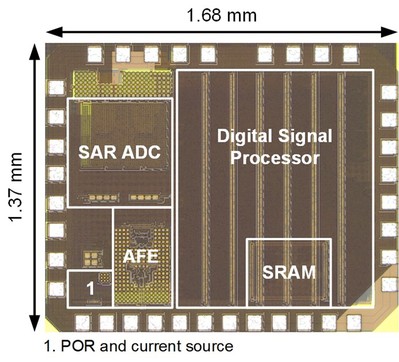
This work presents an ultra-low-power heart rate system-on-a-chip (HR-SoC) for long-term continuous cardiac monitoring applications. A modified QRS complex detection algorithm, verified on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database, achieves a sensitivity of 99.99%, a positive predictive rate of 99.68%, and an accuracy of 99.68% while significantly reducing the power consumption compared to the conventional Pan-Tompkins algorithm. The system outputs averaged HRs (AHRs) and operates in an interrupt-driven architecture, dramatically saving memory resources and power consumption.The HR-SoC integrates an analogfront-end (AFE) forelectrocardiograph (ECG) recording and a digital signal processing (DSP) back-end for QRS detection, storage, and system scheduling and configuration. The AFE strikes a compromiseamong noise, linearity, and power consumption. Fabricated in 0.18-μm CMOS technology, the HR-SoC features acompact area of 1.55 mm2.When operating at a 1-V power supply, it consumes only 1.28-μW in AHR monitoring mode, with 0.48 μW consumed by the AFE and 0.8 μW by the DSP back-end.
本文提出了一种用于长期连续心脏监测的超低功耗心率片上系统(HR-SoC)。通过对MIT-BIH心律失常数据库验证的改进型QRS波群检测算法,在显著降低传统Pan-Tompkins算法功耗的同时,实现了99.99%的灵敏度、99.68%的阳性预测率和99.68%的准确率。该系统采用中断驱动架构输出平均心率(AHR),极大节省了存储资源与功耗。该HR-SoC集成了用于心电图(ECG)采集的模拟前端(AFE)和负责QRS波检测、数据存储及系统调度配置的数字信号处理(DSP)后端。模拟前端在噪声、线性度与功耗之间实现了优化平衡。采用0.18微米CMOS工艺制造的HR-SoC芯片面积仅为1.55平方毫米,在1V电源电压下工作时,AHR监测模式总功耗仅1.28微瓦(其中模拟前端功耗0.48微瓦,DSP后端功耗0.8微瓦)。